By Kure Clinic
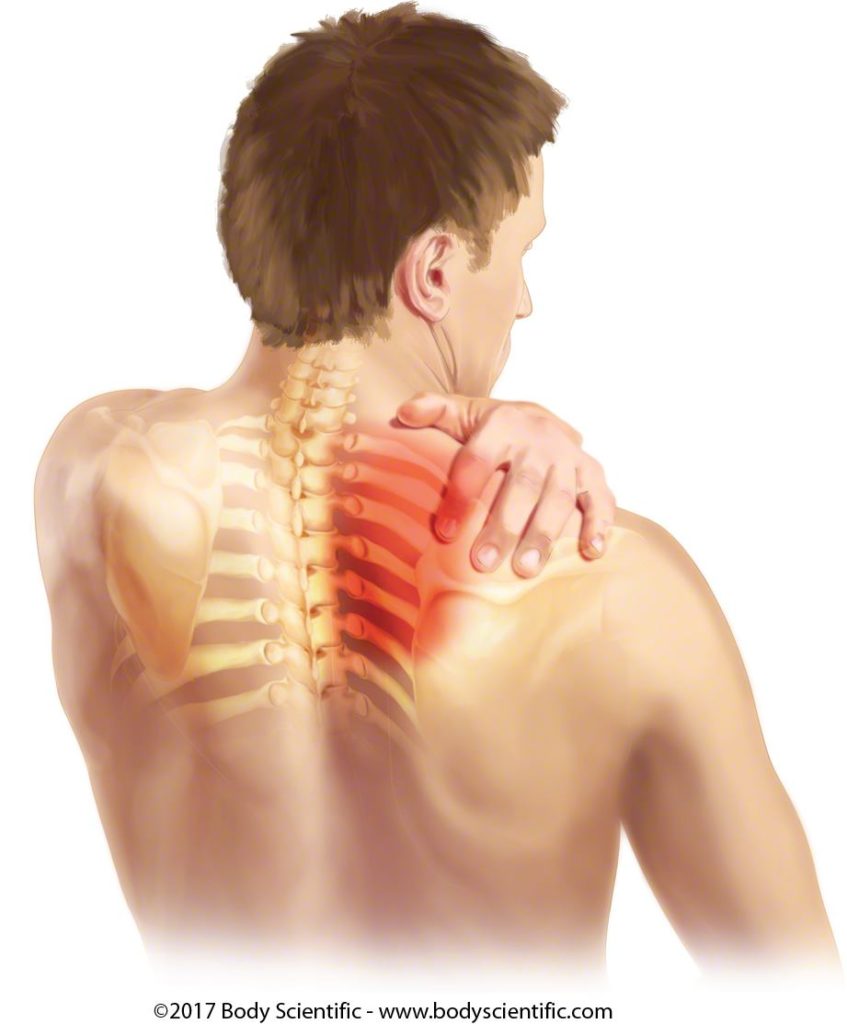
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a condition where there is compression or irritation of the nerves, blood vessels, or both in the thoracic outlet. The thoracic outlet is the space between the collarbone and the first rib. This can result in pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the shoulder, arm, and hand.
There are three types of TOS: neurogenic, vascular, and nonspecific.
Neurogenic TOS is the most common type and occurs when there is compression or irritation of the brachial plexus, a network of nerves that runs from the neck to the armpit and down the arm. This can result in pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the shoulder, arm, and hand.
Vascular TOS occurs when there is compression or irritation of the blood vessels that supply the arm, resulting in pain, swelling, and discoloration in the arm.
Nonspecific TOS is a diagnosis of exclusion when symptoms do not fit into either of the above categories.
The causes of TOS can include physical trauma, repetitive strain injury, poor posture, and anatomical variations such as a cervical rib or abnormal muscles.
The diagnosis of TOS involves a thorough history and physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI, and nerve conduction studies.
Treatment for TOS can involve physical therapy to improve posture and strengthen the shoulder and neck muscles, as well as techniques to reduce nerve compression such as stretching and manual therapy. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the nerves or blood vessels.
SYMPTOMS
The symptoms of thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition.
The most common symptoms of neurogenic TOS include:
The symptoms of vascular TOS include:
Nonspecific TOS can present with a variety of symptoms that may not fit into either category, such as:
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare professional for an evaluation and diagnosis.
CAUSES OF THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
It is important to see a healthcare professional for an evaluation and diagnosis if you are experiencing symptoms of TOS.
ROLE OF PHYSIOTHERAPIST
A physiotherapist can play an important role in the management of thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS). They can help to:
ROLE OF CHIROPRACTOR
Chiropractors may also play a role in the management of thoracic outlet syndrome. They may use manual therapies such as spinal manipulation and mobilization to alleviate joint restrictions and improve mobility in the neck and upper back. They may also use soft tissue techniques to release muscle tension and improve circulation to the affected area. Additionally, chiropractors may prescribe exercises to strengthen the muscles around the shoulder girdle and improve posture, which can help prevent further episodes of thoracic outlet syndrome